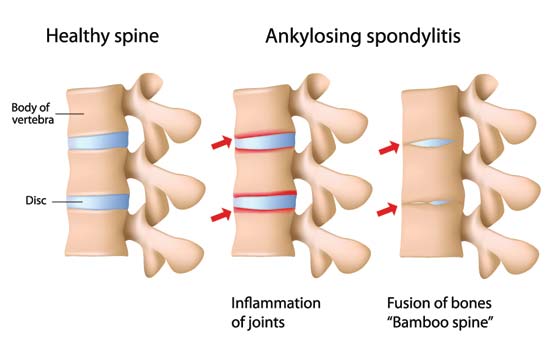
Definition
- A chronic inflammatory disease of the spine that can result in fused vertebrae and rigid spine.
Etiology
- Unknown
- Genetic link
Pathophysiology
- Genetic link
- Ligaments supporting bones become calcified of filled with lime.
- Disease gradually progresses upward until the end of spine
- Spine become stiff
- The upper curve of the spine become more bent
- Muscle spasm occur
Signs and Symptoms
- Lower back pain that is worse at night, in the morning or after inactivity.
- Stiffness and limited motion in lower back pain.
- Hip pain and stiffness.
- Limited expansion of chest.
- Limited range of motion, especially involving spine and hips.
- Joint pain and joint swelling in the shoulders, knees, and ankles.
- Neck pain
- Heel pain
- Chronic stooping to relieve symptoms.
- Fatigue
- Low grade fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Eye inflammation
Assessment
- White blood cells
- Glucose content of synovial fluid decreased
- X-ray
- Synovial fluid analysis or culture and joint fluid.
- Blood culture
- RBC decrease
- Physical examination
- C-reactive protein test
- Immunoglobulin electrophoresis
- Creatinine clearance
Nursing Diagnoses
- Pain
- Impaired physical mobility
- Self-care deficit
- Fatigue
- Activity intolerance
- Potential for injury
- Knowledge defict
- Body image disturbances
Complications
- The jaw about ten percent of people with spondylitis experienced inflammation of the jaw. This can be particularly debilitating causing difficulty in fully opening the mouth to eat.
- Iritis or Anterior Uveitis (inflammation of the eye). About one third of people with spondylitis will experience inflammation of the eye atleast once.
- Spinal rigidity
- Paraspinal calcification
- Respiratory complication
Nursing Interventions
- Apply heat packs at the affected area.
- Provide adequate rest.
- Encourage to perform isometric exercises.
- Provide the patient quiet environment.
- Discuss the factors of his or her present condition.
- Encourage diversional activities.
- Provide foods that are low calories.
- Promote safe physical environment and individual safety.
- Encourage deep breathing exercises.
- Use ambulatory devices.
- Administer analgesics as ordered to control pain.
- Schedule patient walking exercises activities.