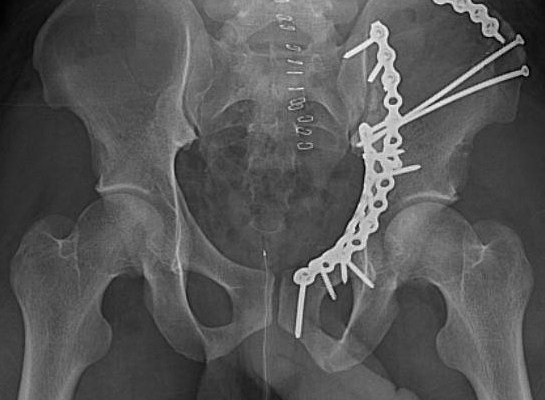
- Usually caused by force applied to the femur which is translated to the acetabulum.
- In young adults, acetabular fractures are due to high energy injuries, primarily motor vehicle accidents.
- The majority of patients are evaluated for and have associated injuries that require initial evaluation of the multiple trauma patient.
- There are also minority of patients, which are elderly, and suffer relatively minor trauma causing acetabular fractures.
Pathophysiology
- Fractures maybe caused by direct trauma to the bone.
- Disruption of blood vessel in cortex periostrum.
- Soft tissue bleeding from damage end of bone.
- Hematoma formation
- Bone tissue death
- Necrosis
- Stimulation of inflammatory response vasodilation
- Exudation of plasma
- Increase leukocytes and infiltration of wbc
Signs and Symptoms
- Crepitus
- Deformity
- Pain
- Tenderness at the site
- Swelling
- Loss of function
- Discoloration
- Dislocation of bone
- Bleeding from an open wound with protrusion of bone ends.
- Fever
- Dysfunction
- Hematoma on the site
- Abnormal or decrease sensation of the affected extremity
- Change in size
- Moderate or severe edema joint point
- Dyspnea
- Rapid weal pulse
- Mental confusion apprehension due to hypoxia
- Mental aberration before signs of infection
- Metabolic disturbance
Assessment
- Remove clothing so that entire extremity may be visualized. Cut clothing along seems when necessary.
- Assess for neurovascular changes distal to fracture.
- Assess for change in length, shape or alignment.
- Support joint extremity at all times; including joints above and below the suspected injury.
- If fracture is impacted the patient may be able to bear weight and walk for a short period of time after the initial injury.
- History of simple fall.
- Decrease range of motion.
- Affected limb shortened abducted and externally rotated.
- Greater thochanter may be displaced into the buttock.
Complications
- Pulmonary embolism
- Fat embolism
- Gas gangrene
- Tetanus
- Loss of bone substance
- Soft tissue interposed between bone ends.
- Infection
- Loss of circulation
- Interrupted or improper immobilization
- Inadequate fixation
- Necrosis due to fixation devices
- Metabolic disturbance
Nursing Diagnoses
- Altered health maintenance
- Risk for infection
- Risk for injury
- Impaired skin integrity
- Impaired tissue integrity
- Self-care deficit
- Impaired physical mobility
- Activity intolerance
- Anxiety
- Pain
- Fear
- Disturbed body image
Nursing Interventions
- Assist the patient or significant others to identify self-care deficits.
- Develop plan with patient for self-care, adapting, and organizing care as necessary.
- Assist the patient to maintain and manage usual health practices during period of wellness or when progressive illness.
- Provide for communication and coordination between the healthcare facility team.
- Monitor lesion or wound daily for changes.
- Promote good nutrition with increase protein intake to facilitate healing.
- Encourage adequate period of rest and sleep.
- Provide devices that aid in comfort or healing.
- Discuss importance of early detection and reporting of changes in condition or any unusual physical discomforts and changes.
- Identify required changes in lifestyle.
- Encourage verbalization of feeling about pain.
- Provide comfort measure like backrubbing.
- Encourage patient to do deep breathing exercises during pain.