 Is a disease when the head of the thighbone (femur) in one hip deteriorates due to insufficient blood supply to the area.
Is a disease when the head of the thighbone (femur) in one hip deteriorates due to insufficient blood supply to the area.- Most frequently affects boys 4 to 10 ears old.
Etiology
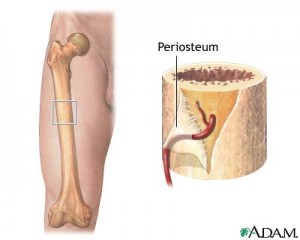
- The blood flow of the femur is interrupted, and the tip of the bone dies over a period of one to three weeks.
- The disorder causes a flattening of the top of the femur (the ball of the head of the femur).
- Usually one hip is affected, although it’s possible for both to develop the condition.
- The disorder may reflect subtle disorders of blood clothing.
Pathophysiology
- Cause of LPD is insufficient blood supply to the femoral head.
- Epiphyseal plate and the ligamentum vessels become nonfunctional.
- Resulting in flattening and collapse of the femoral head.
- Osteonecrosis
Signs and Symptoms
- Knee pain
- Persistent thigh or groin pain
- Atrophy of muscles in the upper thigh
- Slight shortening of the leg, or legs of unequal length.
- Hip stiffness restricting movement in the hip.
- Difficulty walking, walking with limp
- Limited range of motion
- Limited abduction and internal rotation of the hip.
- Mild to moderate muscle spasm.
- Deformity and flattening of femoral head
- Lateral overgrowth of the femoral head cartilage.
- Progressive loss of movement
- Abduction contractures
Assessment
- Physical examination
- Arthrography
- Venography
- MRI
- CT scan
- Ultrasound
- Hip X-ray
Nursing Diagnosis
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Fear
- Impaired physical mobility
- Activity intolerance
- Ineffective role performance
- Low self-esteem
- Social isolation
- Trauma
Nursing Interventions
- Evaluate home and provide guidance to the family regarding the childs home care.
- Encourage family participation to the child’s care so that members can become familiar with details of its management.
- Enable the child to participate as many normal activities of life as possible.
- Plans must be made for continuing education.
- Provide diversional activities.
- Play should include exercise for involved extremities.
- Special activities with peers should be arranged.
- Provide emotional support to the child and his family because of the long term mature of illness.
- Provide the family with frequent opportunities to express their feeling.
- Point out even small indications for recovery process.
- Encourage range of motion exercises.
- Provide bed rest to conserve energy.
Complications
- Osteoarthritis
- Hypothyroidism
- Sickle cell anemia
- Septic arthritis