- Listen to the patient’s fears and concerns.
- Give clear, concise explanations of all procedures and actions, and remain with patient during periods of severe anxiety.
- Encourage patient to identify actions that promote comfort. Then be sure to perform them and to encourage the patient and family to help.
- Include the patient in decisions related to his care whenever possible.
- Administer ordered pain medication as required. Monitor and document the medication’s effectiveness.
- Perform comfort measures, such as repositioning and relaxation techniques.
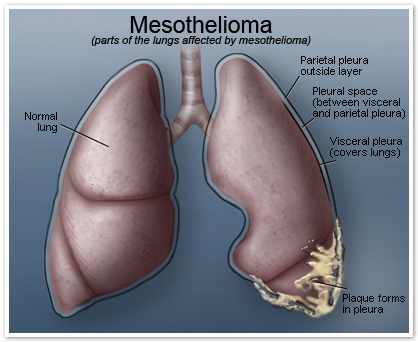
- Monitor respiratory status. Provide oxygen as ordered, and assist the patient to a comfortable position (Fowler’s position, for example) that allows for maximal chest expansion to relieve respiratory distress.
- If mobility decreases, turn the patient frequently. Provide skin care, particularly over bony prominences. Encourage him to be as active as possible.
- Prevent infection. Adhere to strict aseptic technique when suctioning the patient, changing dressings or I.V. tubing, and performing any type of invasive procedure. Monitor body temperature and white blood cell count closely.
- Monitor I.V. fluid intake to avoid circulatory overload and pulmonary congestion.
- Watch for treatment complications by observing and listening to the patient. Also monitor laboratory studies and vital signs. Perform appropriate nursing measures to prevent or alleviate complications. Report complications.
- Show the patient how to perform relaxation techniques. Also demonstrate breathing and positioning variations to ease the dyspnea associated with progressive disease.
- Explain all procedures and treatments. Schedule time to answer the patient’s questions.
- Teach the patient measures (such as increasing fluid intake) to minimize adverse effects of treatment.
- When appropriate, teach the patient and family procedures to maximize breathing and prevent the complications of immobility.
- Explain how to practice meticulous hand washing and aseptic techniques to avoid infection.
- Refer the patient to the social services department, support groups, and community or professional mental health resources to help him and family cope with terminal illness.
- Teach breathing and positioning variations to ease the dyspnea associated with progressive disease
Soures:
https://nanda-nursing.blogspot.com/2011/08/nursing-care-plan-for-mesothelioma.html
https://nursing-concept.blogspot.com/search/label/NURSING%20INTERVENTIONS
https://nursing-media.blogspot.com/2011/09/nursing-diagnosis-and-nursing.html