- Encourage bed rest since it reduces myocardial oxygen demand and usually continues until the following criteria are met:
> Temperature remains normal without use of salicylates
> Resting pulse rate remains less than 100 beats/min
> ECG tracings show no manifestations of myocardial damage
> Pericardial friction rub is not present
- Obtain a clear description of the pain or discomfort. Identify the source of greatest discomfort as a focus for intervention.
- Administer analgesics as needed and use salicylates around the clock. Balance rest and activity according to the degree of pain and activity tolerance.
- Provide psychosocial support while patient is confined to hospital or home with restrictive intravenous therapy.
- If patient received surgical treatment, provide postsurgical care and instruction.
- After surgery, monitor patient’s temperature; a fever may be present for weeks.
- A high-protein, high-carbohydrate diet helps maintain adequate nutrition in the presence of fever and infection.
- Oral hygiene every 4 hours; small, attractive meal servings and foods that are not overly rich, sweet or greasy stimulate the appetite.
- Instruct the client about how to reduce exposure to infection as follows:
- Advise patient to take good care of the teeth and gums, obtain prompt dental care for cavities and gingivitis
- Prophylactic medication may be needed before invasive dental procedures, and individualized evaluation for prophylaxis medication is needed.
- Instruct patient to Avoid people who have an upper respiratory tract infection
- Assess for signs and symptoms of organ damage such as stroke (CVA, brain attack), meningitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction, glomerulonephritis, and splenomegaly.
- Instruct patient and family about activity restrictions, medications, and signs and symptoms of infection.
- Provide a quiet environment and comfort measures such as: change of position, rub his back, use warm compresses / cold, emotional support to reduce physical and emotional discomfort of the patient.
- Refer to home care nurse to supervise and monitor intravenous antibiotic therapy in the home.
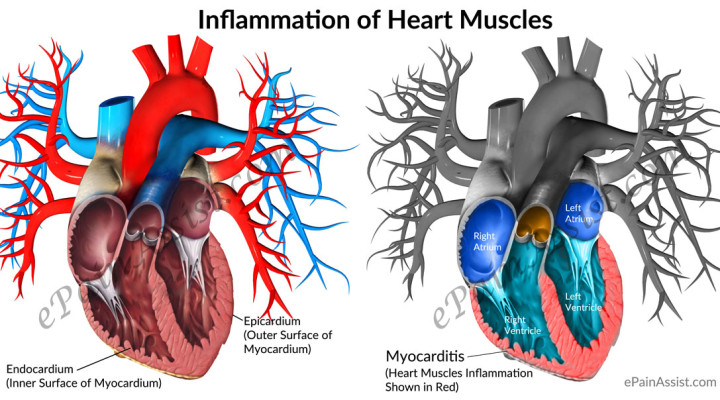
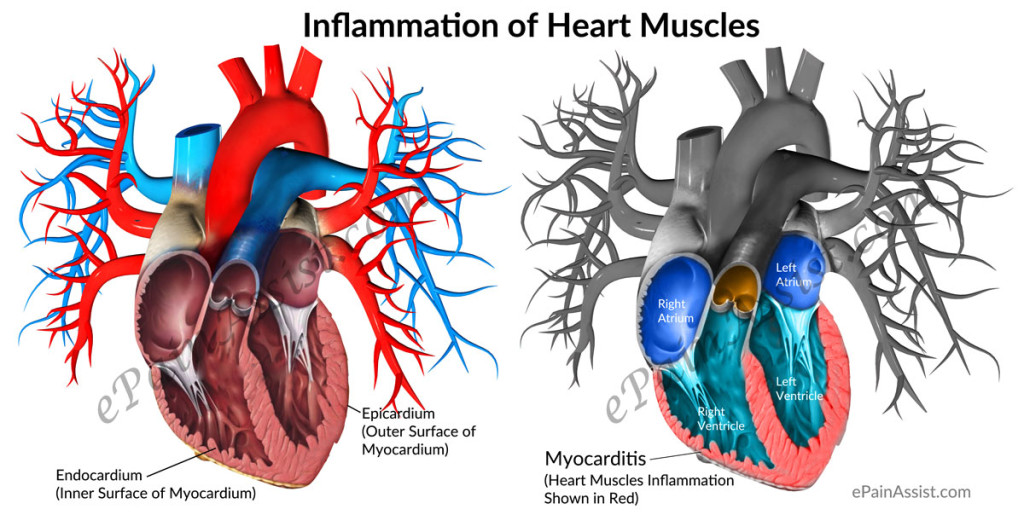






Please send me the information via the above email..thanks
very interesting topics discussions