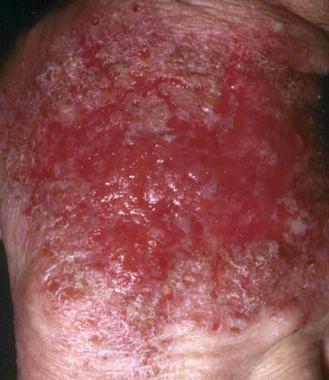
Nursing Interventions for Contact Dermatitis
Keep the patient’s nails cut short. Cutting the nail will reduce skin damage due to scratching. Apply lotions and creams skin immediately after bathing.Hydration is effective in preventing disruption of the stratum corneum layer of the skin barrier. Protect the patient’s skin from the the possibility of maceration (excessive hydration of the stratum corneum) when […]







Recent Comments