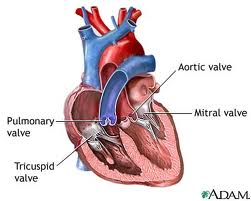
 Nursing Interventions: Endocarditis
Nursing Interventions: Endocarditis
- Watch for signs and symptoms of embolization such as hematuria, pleuritic chest pain, left upper quadrant pain, and paresis.
- Monitor the patient’s renal status including blood urea nitrogen levels, creatinine clearance levels and urine output.
- Assess cardiovascular status frequently and watch for signs of left ventricular failure such as dyspnea, hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, crackles, neck vein distention, edema, and weight gain.
- Check for changes in cardiac rhythm or conduction.
- Evaluate arterial blood gas values as needed to ensure adequate oxygenation.
- Observe for signs of infiltration or inflammation at the venipuncture site.
- Stress the importance of taking the medication and restricting activities for as long as the doctor orders.
- Tell patient to watch closely for fever, anorexia, and other signs of relapse for about 2 weeks after treatment stops.
- Teach the patient how to recognize symptoms of endocarditis, and tell him to notify the doctor immediately if such symptoms occur.
- Stress the importance of dental hygiene to prevent caries and possible recurrent endocarditis.






Embilization symptom:
hematuri or hemoptesis