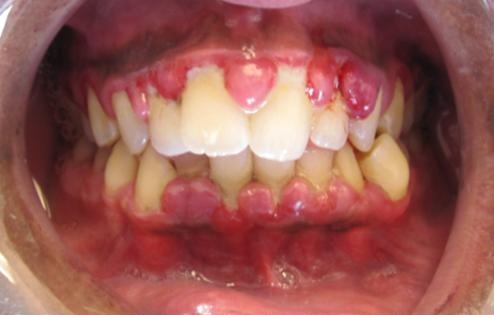
- Inspect oral cavity at least once daily and note any discoloration, lesions, edema, bleeding, exudate, or dryness. Refer to a physician or specialist as appropriate. (Oral inspection can reveal signs of oral disease, symptoms of systemic disease, drug side effects, or trauma of the oral cavity)
- Assess for mechanical agents such as ill-fitting dentures or chemical agents such as frequent exposure to tobacco that could cause or increase trauma to oral mucous membranes. (Irritative and causative agents for stomatitis should be eliminated)
- Monitor client’s nutritional and fluid status to determine if adequate. (Dehydration and malnutrition predispose clients to impaired oral mucous membranes.)
- Encourage fluid intake up to 3000 ml per day if not contraindicated by client’s medical condition (Fluids help increase moisture in the mouth, which protects the mucous membranes from damage and helps the healing process)
- Determine client’s mental status. If client is unable to care for self, oral hygiene must be provided by nursing personnel.
- Determine client’s usual method of oral care and address any concerns regarding oral hygiene. (Whenever possible, build on client’s existing knowledge base and current practices to develop an individualized plan of care.)
- Educate the patient about avoiding, mouthwashes with high alcohol content, lemon swabs or prolonged use of hydrogen peroxide.
- If client does not have a bleeding disorder and is able to swallow, encourage to brush teeth with a soft pediatric-sized toothbrush using a fluoride-containing toothpaste after every meal and to floss teeth daily. (The toothbrush is the most important tool for oral care. Brushing the teeth is the most effective method for reducing plaque and controlling periodontal disease)
- Use tap water or normal saline to provide oral care; do not use commercial mouthwashes containing alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. Also, do not use lemon-glycerin swabs. (Alcohol dries the oral mucous membranes Hydrogen peroxide can damage oral mucosa and is extremely foul tasting to clients. Lemon-glycerin swabs can result in decreased salivary amylase and oral moisture, as well as erosion of tooth enamel)
- Use foam sticks to moisten the oral mucous membranes, clean out debris, and swab out the mouth of the edentulous client. Do not use to clean the teeth or else the platelet count is very low, and the client is prone to bleeding gums. (Studies have shown that foam sticks are probably not effective for removing plaque from teeth. However, they are useful for cleaning the mouth of the edentulous client)
- If client’s oral cavity is dry, the keep inside of the mouth moist with frequent sips of water and salt water rinses (1/2 tsp salt in 8 oz of warm water) or artificial saliva. (Moisture promotes the cleansing effect of saliva and helps avert mucosal drying, which can result in erosions, fissures, or lesions. Sodium chloride rinses have been shown to be effective for the prevention and treatment of stomatitis)
- If mouth is severely inflamed and it is painful to swallow, contact the physician for a topical anesthetic agent or analgesic order. Modification of oral intake (e.g., soft or liquid diet) may also be necessary to prevent friction trauma.
- Educate the patient on 3 ways on how to relieve dry mouth by discharge.
- If whitish plaques are present in the mouth or on the tongue and can be rubbed off readily with gauze, leaving a red base that bleeds, suspect a fungal infection and contact the physician for follow-up. (Oral candidiasis (moniliasis) is extremely common secondary to antibiotic therapy, steroid therapy, HIV infection, diabetes, or immunosuppressive drugs and should be treated with oral or systemic antifungal agents)
Sources:
https://nursinginterventionsrationales.blogspot.com/2013/08/impaired-oral-mucous-membrane.html
https://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/gingivitis/overview.html