Computer Data Processing
- Any computing process that transforms patient and healthcare data into information of knowledge necessary for the medication use process.
- Manipulates raw data into information necessary for the health industry and computer information systems typically take raw data as input to the system to produce information as output.
- Equipped with facility that remotely accessing data and translate it using the statistical information such as charts, table, index, and forecast.
Statistical Information System
- Basic tool for the nursing informatics system to processes the data via computer means.
Data
- Characters that represent measurement or that can be quantifiable from observable condition such as dimension, amount, capacity, height, weight, length or any number
- The measured data is then feed to system, such as statistical information system, to statistically transform it to necessary information.
Information
- Meaningful answer to a query or a meaningful stimulus that can cascade further queries.
Data Processing
- The process of transforming data into information.
Data Analysis
- Data transformation into useful information, the healthcare officer or nurse should carefully examine the information and should be able to interpret the harvested information to proper application.
- The healthcare giver or nurse should not divulge or disclosed the information from the others since these data or information are owned by the hospital, clinics, and the patient.
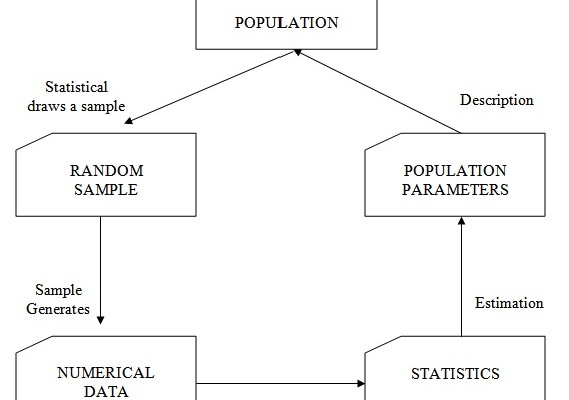
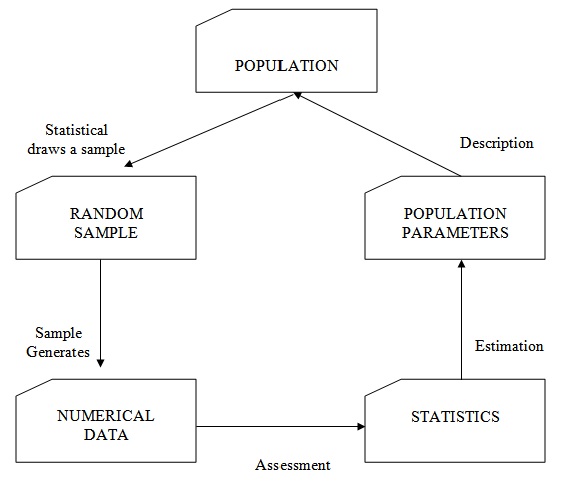
Procedure for Statistic Study
- Use to describe the samples from the population, and to draw conclusion or inferences about the population from which the sample is drawn.
- Decisions made concerning the population based on sample information are based on probability.
Process of Conducting Statistical Analysis
Advantages of Survey
- It is an efficient way of collecting information from a large number of respondents
- Surveys are flexible in the sense that a wide range of information can be collected
- Free from errors
- They are relatively easy to administer
- There is an economy is data collection
- Maximization of time
Disadvantages of Survey
- They depend on subject motivation, honesty, memory, and ability to respond.
- Low validity of results
- Errors due to non-responsive
- Vague data sets
- Non-conclusive results due to choice of data