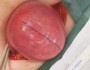
Definition: inflammation of the wall of a vein with associated thrombosis, often occurring in the legs during pregnancy. 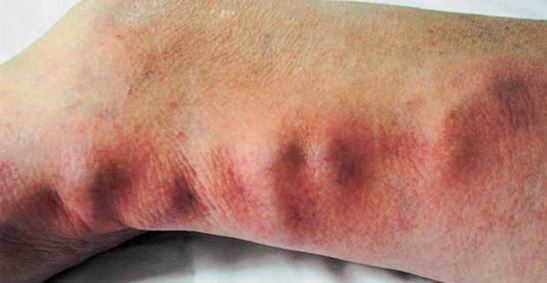
- Evaluate circulatory and neurological studies of involved extremity—both sensory and motor. Inspect for skin color and temperature changes, as well as edema (from groin to foot). Note symmetry of calves; measure and record calf circumference. Report proximal progression of inflammatory process, traveling pain.
- Examine extremity for obviously prominent veins. Palpate gently for local tissue tension, stretched skin, knots/bumps along course of vein.
- Assess capillary refill and check for Homans’ sign.
- Promote bedrest initially, with legs elevated above heart level during acute phase
- Elevate legs when in bed or chair, as indicated.
- Initiate active or passive exercises while in bed (e.g., flex/extend/rotate foot periodically). Assist with gradual resumption of ambulation (e.g., walking 10 min/hr) as soon as patient is permitted out of bed.
- Caution patient to avoid crossing legs or hyperflexion at knee (seated position with legs dangling, or lying in jackknife position)
- Instruct patient to avoid rubbing/ massaging the affected extremity
- Encourage deep-breathing exercises
- Increase fluid intake to at least 2000 mL/day, within cardiac tolerance
- Apply warm, moist compresses or heat cradle to affected extremity if indicated.
- Administer anticoagulants, e.g.:Heparin, e.g., Panheparin or low molecular weightheparin (LMWH), such as enorxaparin (Lovenox),dalteparin (Fragmin), ardeparin (Normiflo) viacontinuous or intermittent IV, intermittentsubcutaneous (SC) injections, and/or PO coumarinderivatives, e.g., warfarin (Coumadin) or dicumarol(Sintrom) as ordered.
- Administer Thrombolytic agents, e.g., streptokinase, urokinase as ordered.
- Monitor laboratory studies as indicated: PT, PTT, aPTT, CBC, as well as Platelet count, platelet/aggregation test, anti-heparin antibody assay
- Apply/regulate graduated compression stockings, intermittent pneumatic compression, if indicated.
- Apply elastic support hose following acute phase. Take care to avoid tourniquet effect.
- Prepare for surgical intervention when indicated
- If the patient is being discharged on subcutaneous heparin, the patient or family needs to demonstrate the injection technique.
- The patient also needs to know to avoid over-the-counter medications, particularly those that contain aspirin.
- Explain the need to avoid activities that could cause bumping or injury and predispose the patient to excessive bleeding.
- Instruct the patient to notify the physician if abdominal or flank pain, heavy bleeding during menstruation, and bloody urine or stool occurs.
- Recommend using a soft toothbrush and an electric razor to limit injury.
- Remind the patient to notify the physician or dentist of anticoagulant use before any invasive procedure.
- Instruct the patient to report leg pain or swelling, skin discoloration, or decreases in peripheral skin temperature to the physician.
- In addition, if the patient experiences signs of possible pulmonary embolism (anxiety, shortness of breath, pleuritic pain, hemoptysis), he or she should go to the emergency department immediately.