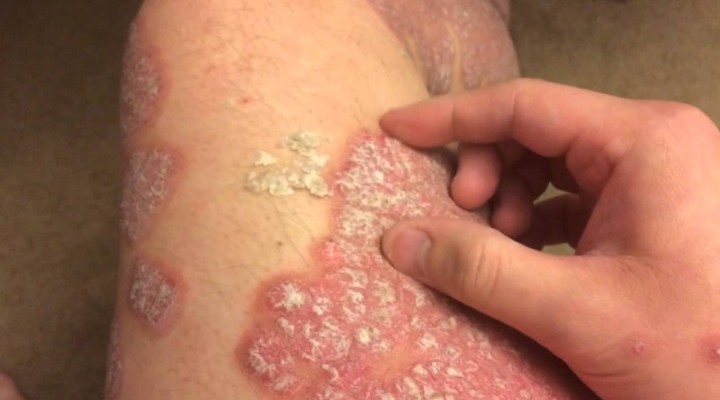
- Examine skin condition.
- Monitor vital signs.
- Assess skin color changes.
- Examine for signs of infection.
- Instruct the patient to not pinch or scratch the skin area
- Keep the infected area clean and dry.
- Reduce the formation of scales with the provision of bath oil
- Patient’s motivation for consuming nutrients: high in calories and high in protein.
- Administer prescribed medications, which may include coal tar therapy, and topical corticosteroids.
- Discuss and assist with the administration of additional medical treatments, which may include coal tar shampoos, intralesional therapy (i.e. injection of medication directly into lesion), systemic cytotoxic medication, photochemotherapoy, occlusive dressing.
- Enhance skin integrity
- Prevent infection.
- Provide client and family teaching.
- Advise the client receiving systemic cytotoxic (e.g. methotrexate) therapy, which inhibits deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in epidermal cells to speed the replacement of psoriatic cells, to continue taking the medication even if nausea and vomiting occur, to increase fluid intake to prevent nephrotoxicity, and to avoid alcoholic beverages.
- Instruct the client to avoid sun exposure during photochemotherapy. This regimen of phototherapy with ultraviolet A (PUVA) light decreases cellular proliferation. PUVA therapy results in photosensitivity and the client should avoid exposure to sunlight during this time.
- Be knowledgeable about treatment, and give the client written instructions.
- Support the preferred type of coping when the adaptive mechanism is used
- Encourage patient to express his feelings. Give the patient time to express the problem and the encouragement of free expression, such as anger, fear, doubt
- Explain all procedures and treatments
Sources:
- https://www.nursing-nurse.com/medical-and-nursing-management-of-psoriasis-356/
- https://free-nursingcareplan.blogspot.com/2011/07/nursing-care-plan-for-psoriasis.html