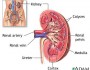
Nursing Interventions: Hyperparathyroidism
- Obtain baseline serum potassium, calcium, phosphate, and magnesium levels before treatment.
- Provide atleast 3 liters of fluid per day, including cranberry or prune juice, to increase urine acidity and help prevent calculus formation.
- Take safety precaution to minimize the risk for injury from fall.
- Schedule care to allow the patient with muscle weakness as much rest as possible.
- Provide comfort measures to alleviate bone pain.
- Administer antacids, as appropriate to prevent pelvic ulcers.
- Auscultate the lungs regularly. Check for signs of pulmonary edema in the patient receiving large amounts of normal saline solution, especially if he has pulmonary or cardiac disease.
- Check for elevated serum calcium levels if the patient is receiving cardiac glycosides.
- Assess the patient for parathyroid poisoning, musculoskeletal changes, and renal impairment.
- Observe the patient for signs of pain and monitor him for effectiveness of analgesics and comfort measures.