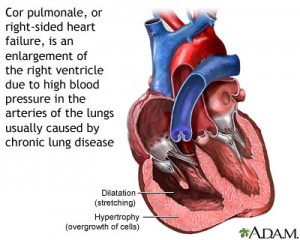
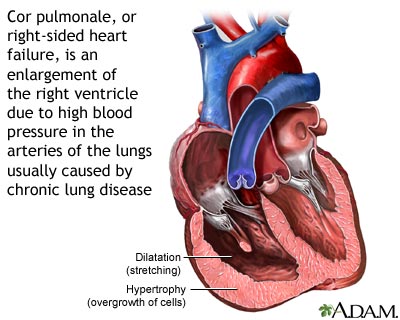
 Nursing Interventions: Cor Pulmonale
Nursing Interventions: Cor Pulmonale
- Listen to the patient’s fears and concerns about his illness.
- Plan a nutritious diet carefully with the patient and the staff dietitian.
- Prevent fluid retention by limiting the patient’s fluid intake to 1,000 to 2,000 ml daily and providing a low sodium diet.
- Reposition the bed ridden patient often to prevent atelectasis.
- Provide meticulous respiratory care, including oxygen therapy and for COPD patients.
- Pace patient care activities to avoid patient fatigue.
- Monitor serum potassium levels closely if the patient takes a diuretic.
- Be alert for complaints that signal digoxin toxicity, such as anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and seeing a yellow halo around an object.
- Measure ABG levels and watch for signs of respiratory failure as change in pulse rate, deep labored respirations; and increased fatigue produced by exertion.
- Instruct the patient to schedule frequent rest periods and to perform his breathing exercises regularly.






please share with me the information through my email. i will graetly appreciate