- Take patient history and perform assessment.
- Monitor vital signs especially blood pressure.
- Monitor renal function and urine elimination, hydration, fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Monitor daily weights
- Assess edema and promote skin integrity.
- Access site for dialysis (if appropriate)
- Give prescribed drugs, including ACE inhibitors to control hypertension (if giving diuretics, obtain specimens for serum electrolyte levels, especially potassium, which may be decreased)
- Provide comfort measures, including opioid analgesics; assist the patient with relaxation techniques and the use of TENS.
- Provide fluids and foods based on the patient’s condition, encourage increased fluids if the patient has a urinary tract infection, and restrict fluids if the patient has renal failure.
- Provide supportive care to minimize symptoms.
- Obtain specimens for urinalysis and culture and sensitivity as ordered to evaluate for hematuria, proteinuria, and infection; obtain specimens for laboratory tests, such as electrolyte levels, as ordered.
- Individualize patient care, as appropriate
- Allow the patient to verbalize his feelings and concerns, especially related to possible progression of the disease and renal failure; provide support and guidance.
- Prepare the patient for dialysis or renal replacement therapy as indicated.
- Encourage the parents of a child with the infantile form to obtain genetic counseling.
- Prepare the patient and his family for possible renal transplant or surgery.
- Refer the patient and his family to community and social services for support.
Sources:
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystic-kidney-disease-flash-cards/
https://ce4nurses.org/chronic-kidney-disease-stages-and-nursing-care/
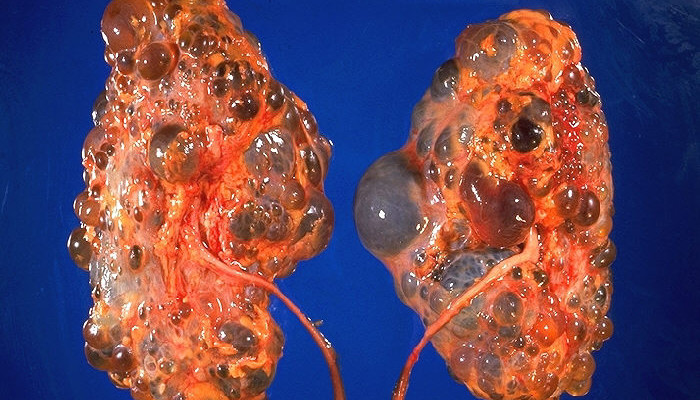
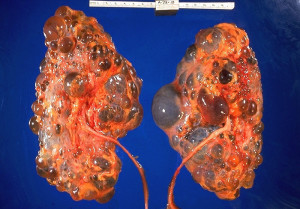






Policystic kidney
Como puedo curarme