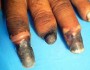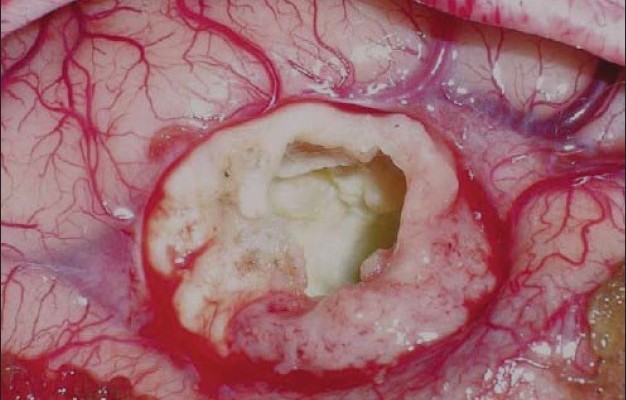
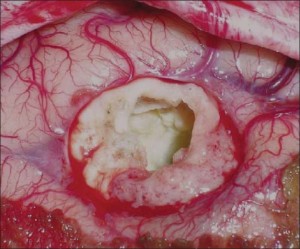
 Obtain a thorough history of the patient including history of infections
Obtain a thorough history of the patient including history of infections- Nursing interventions should support the medical treatment, as do patient teaching activities that address neurosurgical procedures.
- Advise patients and families of neurologic deficits that may remain after treatment (hemiparesis, seizures, visual deficits, and cranial nerve palsies).
- Frequently assess neurologic status, especially LOC, speech and sensorimotor and cranial nerve functions.
- Administer antimicrobial medications as ordered.
- Administer insulin or electrolyte replacement (as ordered) to return this values to the normal state.
- Blood laboratory test results especiallyblood glucose and serum potassium levels has to be monitored.
- Watch out for signs of increased ICP: decreased LOC, vomiting, abnormal pupil response and depressed respirations.
- Observe for neurological deficits like hemiparesis,seizures,visual deficits etc..
- Constantly monitor the level of consciousness and the physical status
- Assess patient’s response to the treatment and provide supportive care
- Assess the family’s ability to express their distress at the patient’s condition, cope with the patient’s illness and deficits, and obtain support.
- Always provide safety measures
 Obtain a thorough history of the patient including history of infections
Obtain a thorough history of the patient including history of infections